Non-digestible oligosaccharides partially prevent the development of LPS-induced lung emphysema in mice - ScienceDirect

Acute Lung Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Is Independent of Complement Activation | The Journal of Immunology

Monitoring lung injury with particle flow rate in LPS‐ and COVID‐19‐induced ARDS - Stenlo - 2021 - Physiological Reports - Wiley Online Library

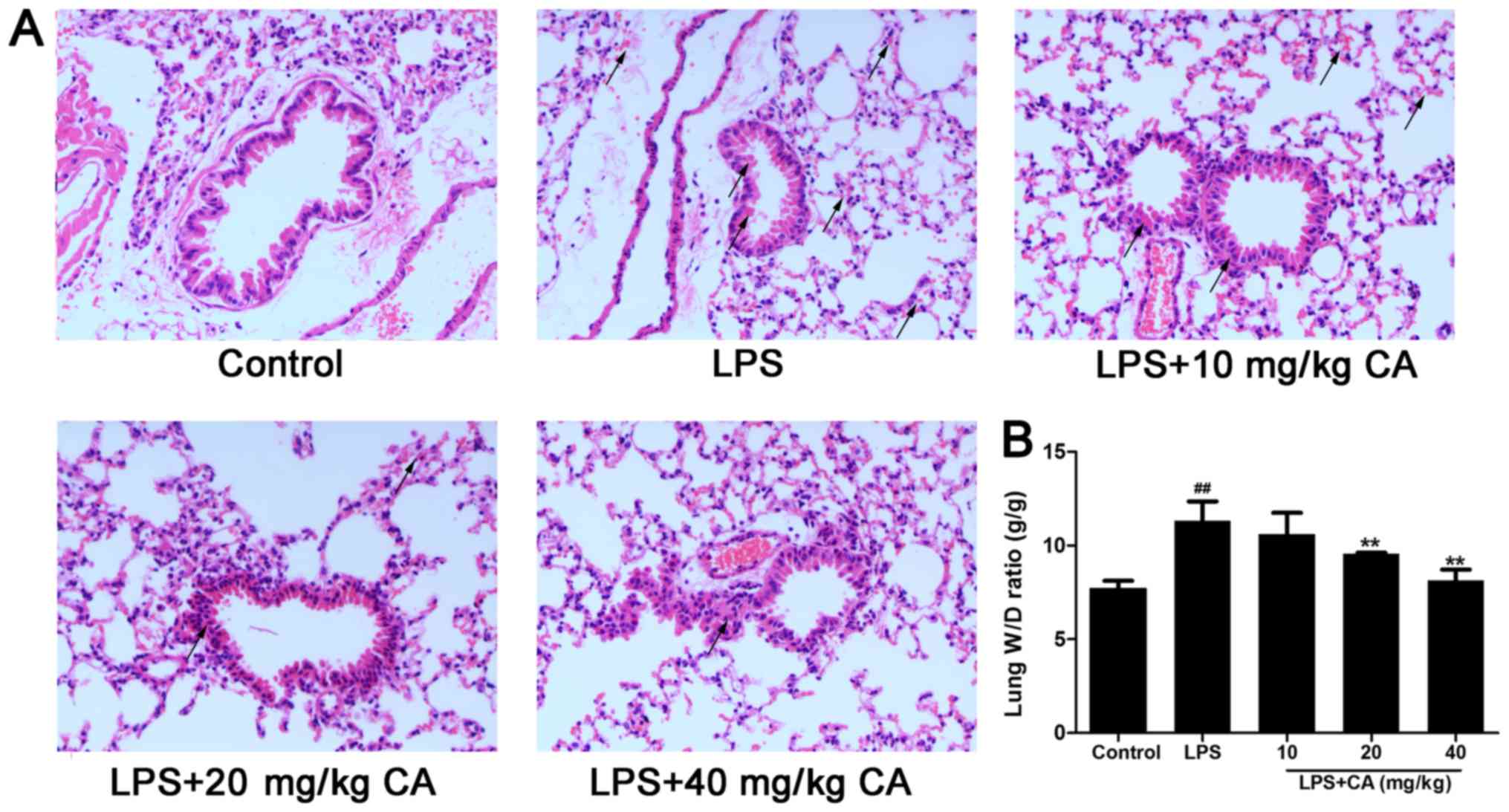
Effects of CH on LPS-induced lung injury in mice. (A) Representative... | Download Scientific Diagram

Serum amyloid A promotes LPS clearance and suppresses LPS‐induced inflammation and tissue injury | EMBO reports

Lung inflammation promotes metastasis through neutrophil protease-mediated degradation of Tsp-1 | PNAS
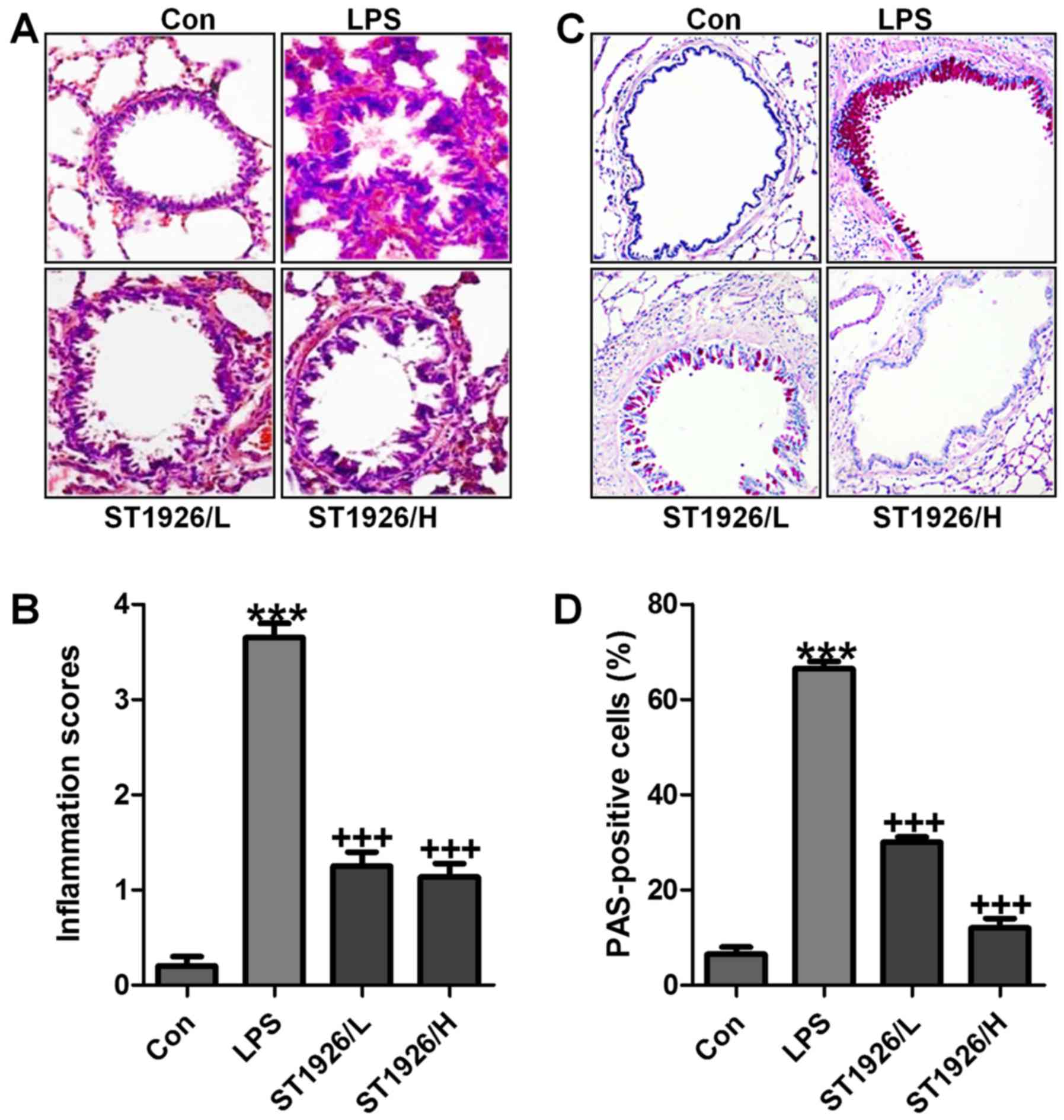
Accelerated inflammation and oxidative stress induced by LPS in acute lung injury: Ιnhibition by ST1926
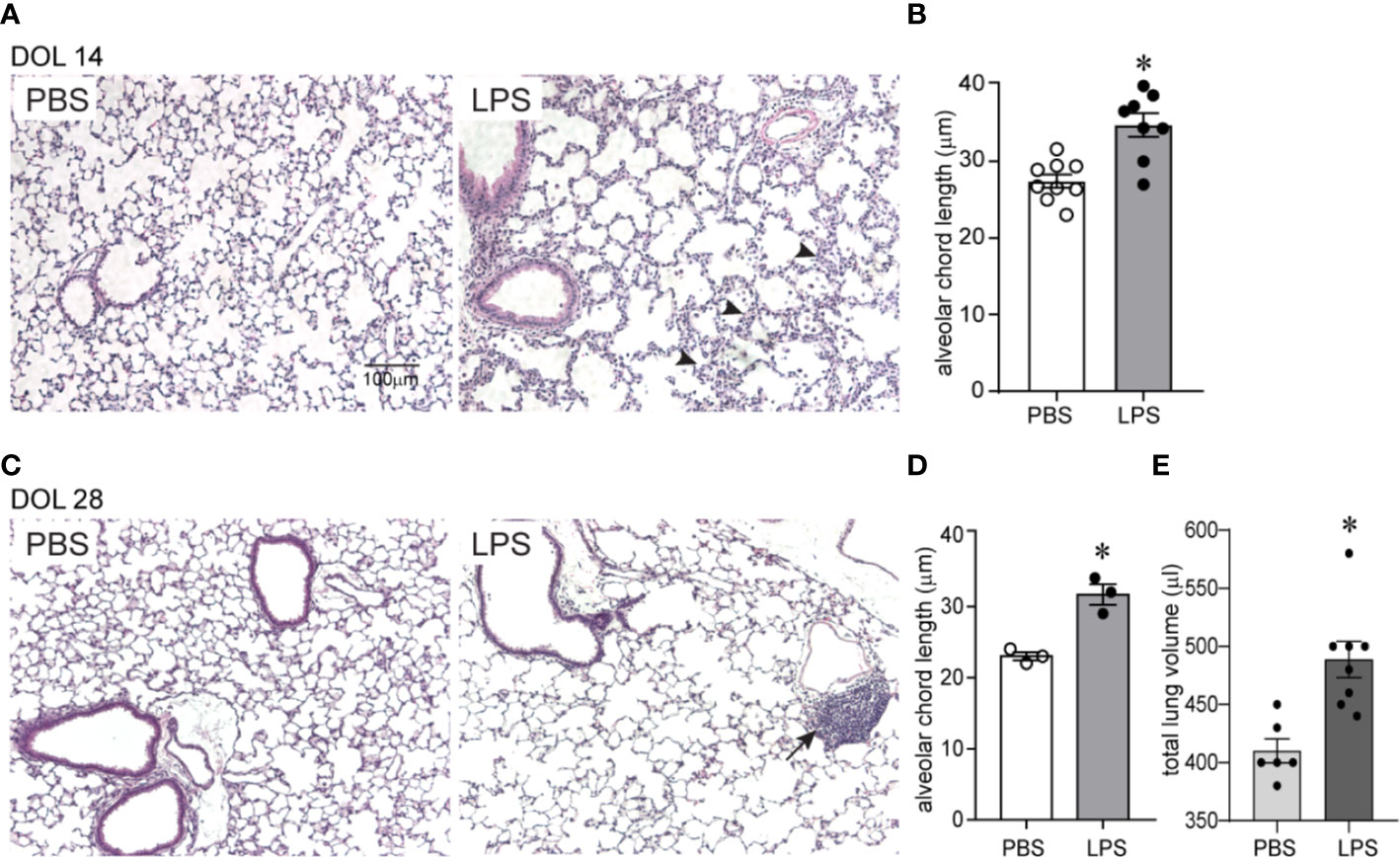
Frontiers | CCR2 Mediates Chronic LPS-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Hypoalveolarization in a Murine Model of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia | Immunology
Inhibition of complement C5a receptor protects lung cells and tissues against lipopolysaccharide-induced injury via blocking pyroptosis | Aging

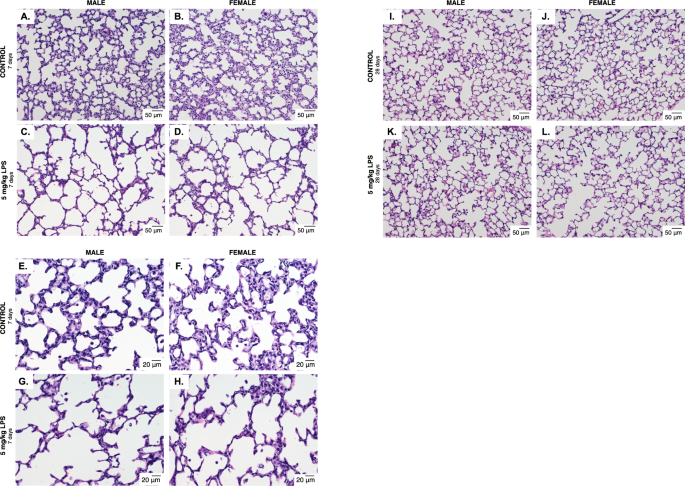
LPS induces increased lung inflammation in adult versus neonatal mice.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Comparison of direct and indirect models of early induced acute lung injury | Intensive Care Medicine Experimental | Full Text

Fucoidan inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice through regulating GSK-3β-Nrf2 signaling pathway | SpringerLink

Acute Lung Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Is Independent of Complement Activation | The Journal of Immunology

Berberine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide‐induced acute lung injury via the PERK‐mediated Nrf2/HO‐1 signaling axis - Liang - 2019 - Phytotherapy Research - Wiley Online Library
Receptor Interacting Protein 3-Mediated Necroptosis Promotes Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Mice | PLOS ONE
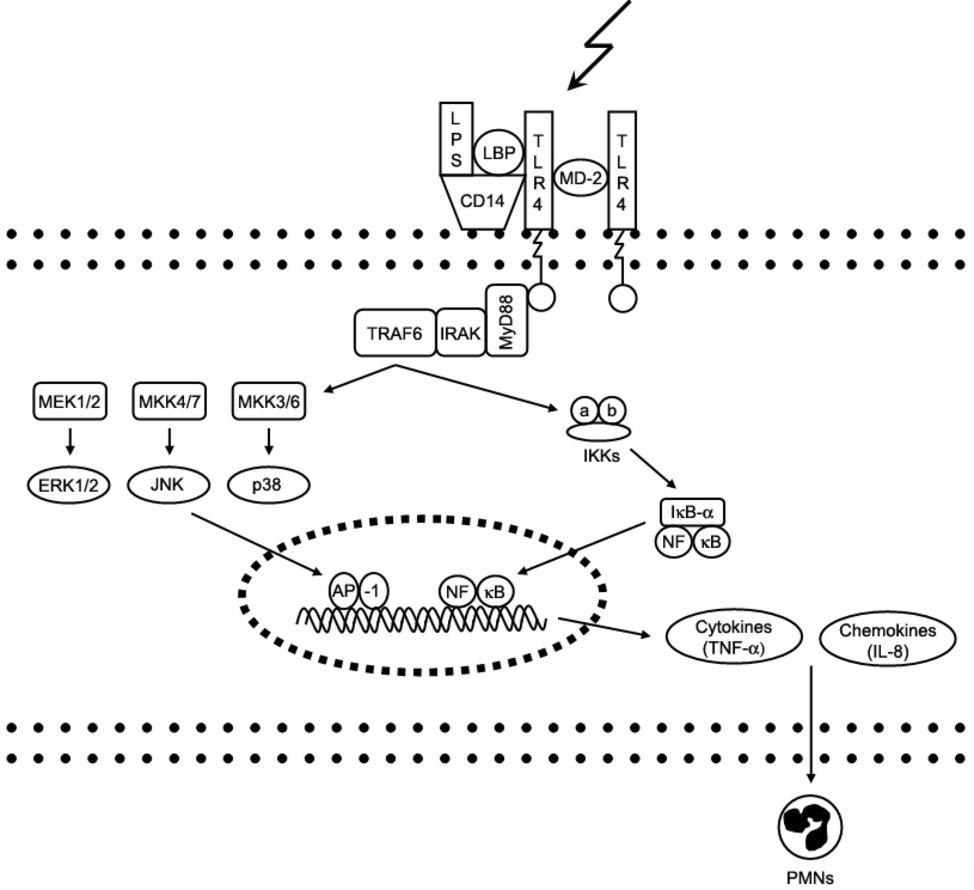
PARP-1 Inhibitor, DPQ, Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Inhibiting NF-κB-Mediated Inflammatory Response | PLOS ONE

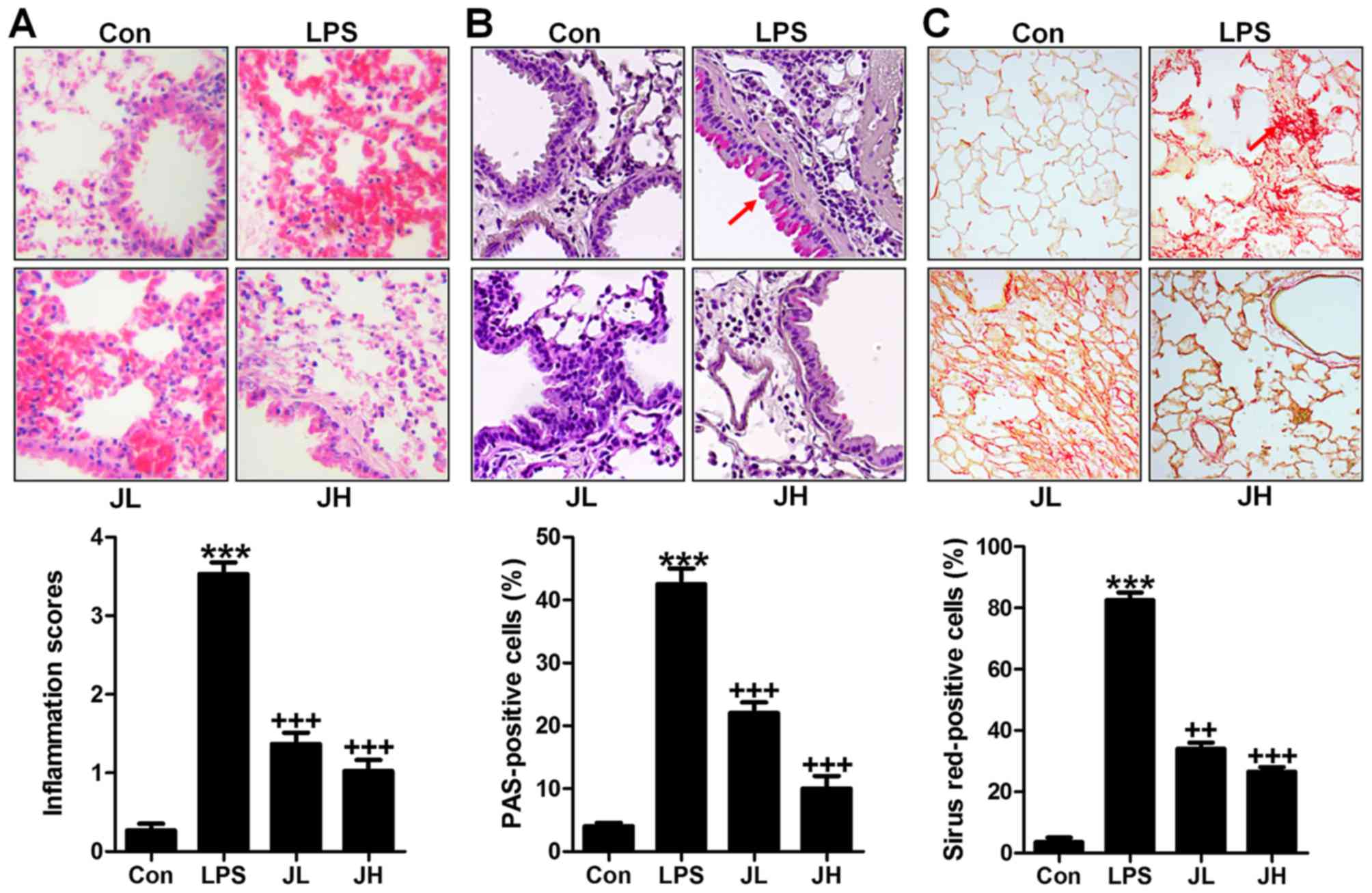
Emodin alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory response in lung injury rat by affecting the function of granulocytes | Journal of Inflammation | Full Text