Retinoic Acid Receptor- Alpha and Its Role in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia By Alex Sheng. - ppt download

Teratogen update: Topical use and third‐generation retinoids - Williams - 2020 - Birth Defects Research - Wiley Online Library
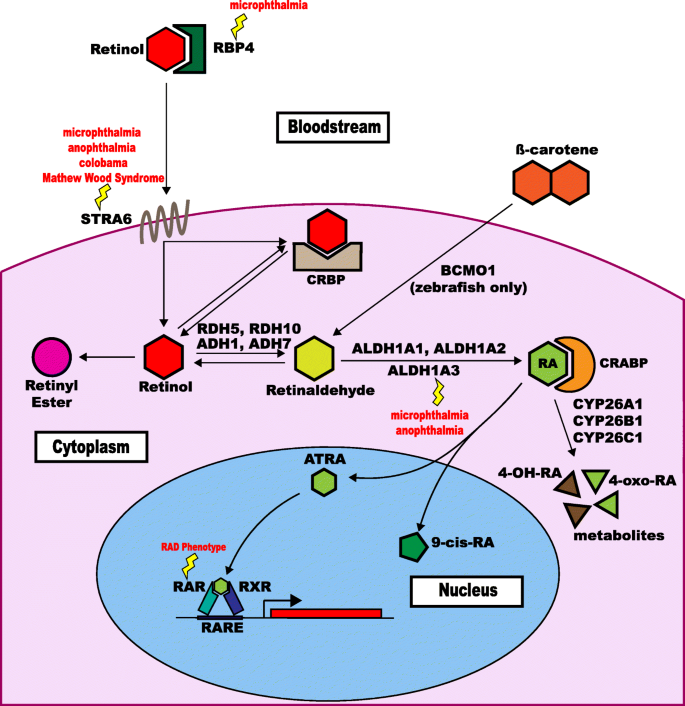
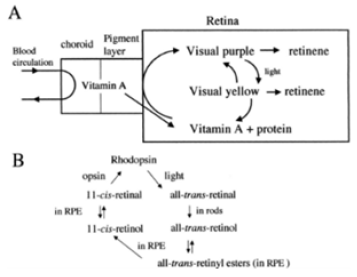
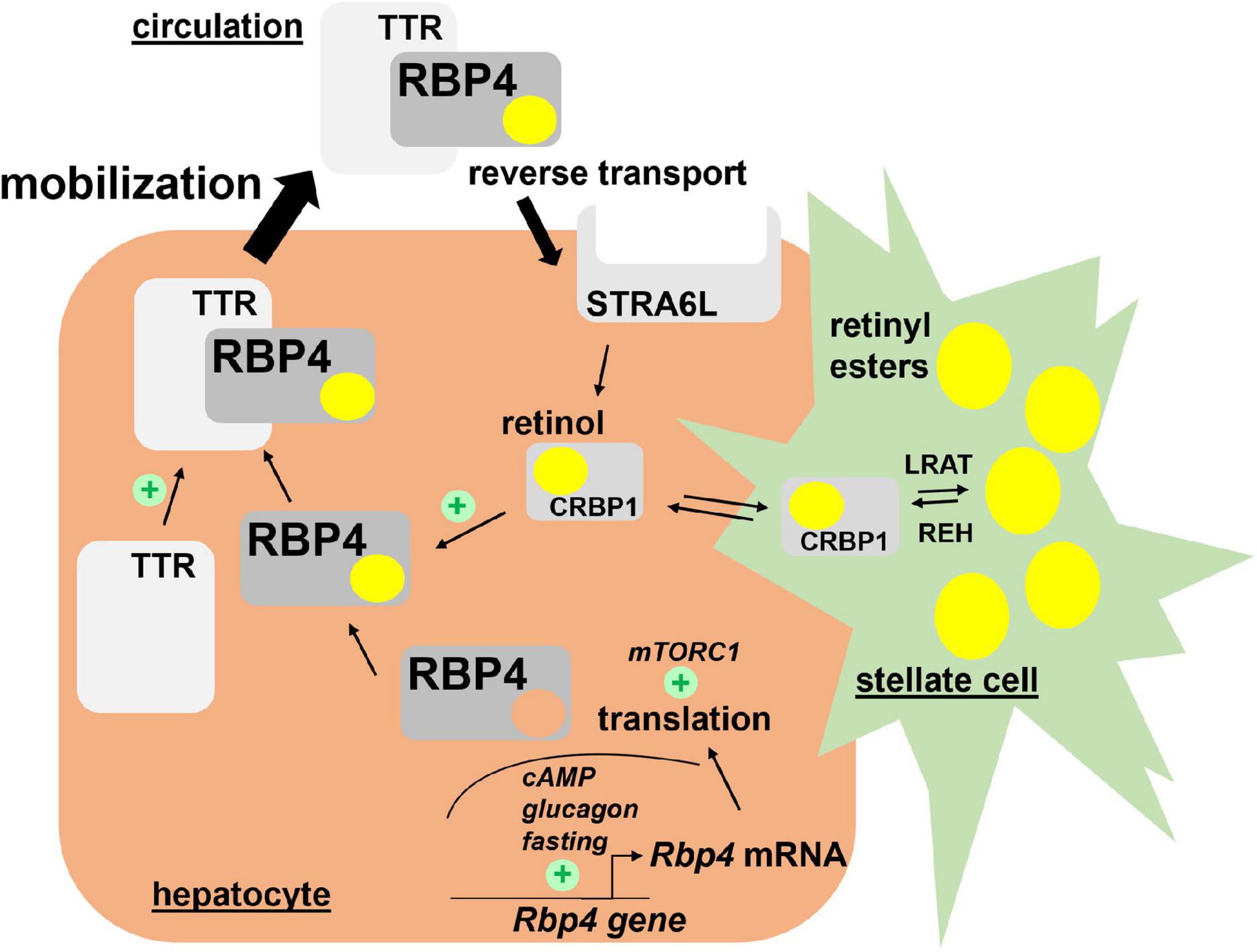
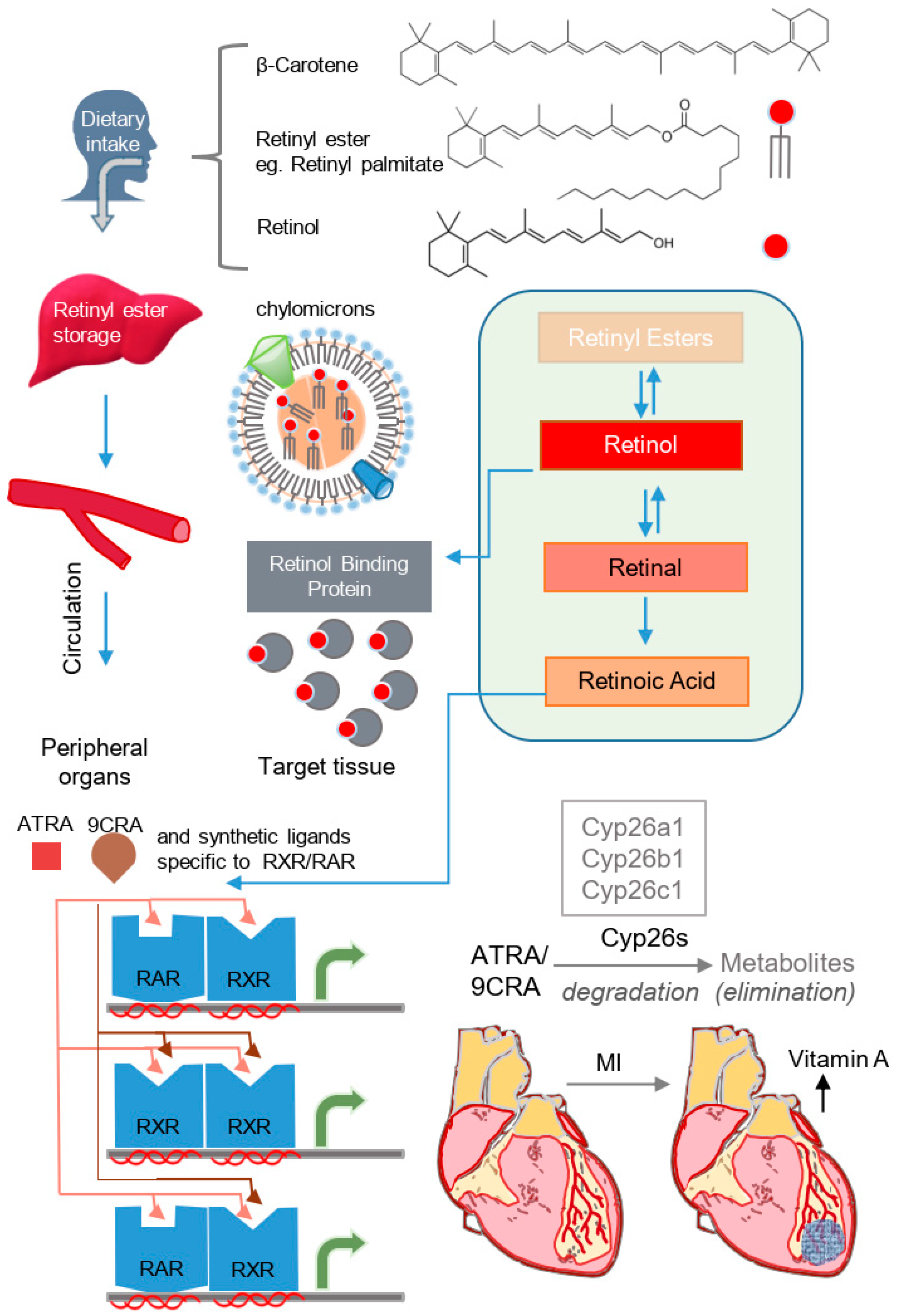
Genetics and functions of the retinoic acid pathway, with special emphasis on the eye | Human Genomics | Full Text

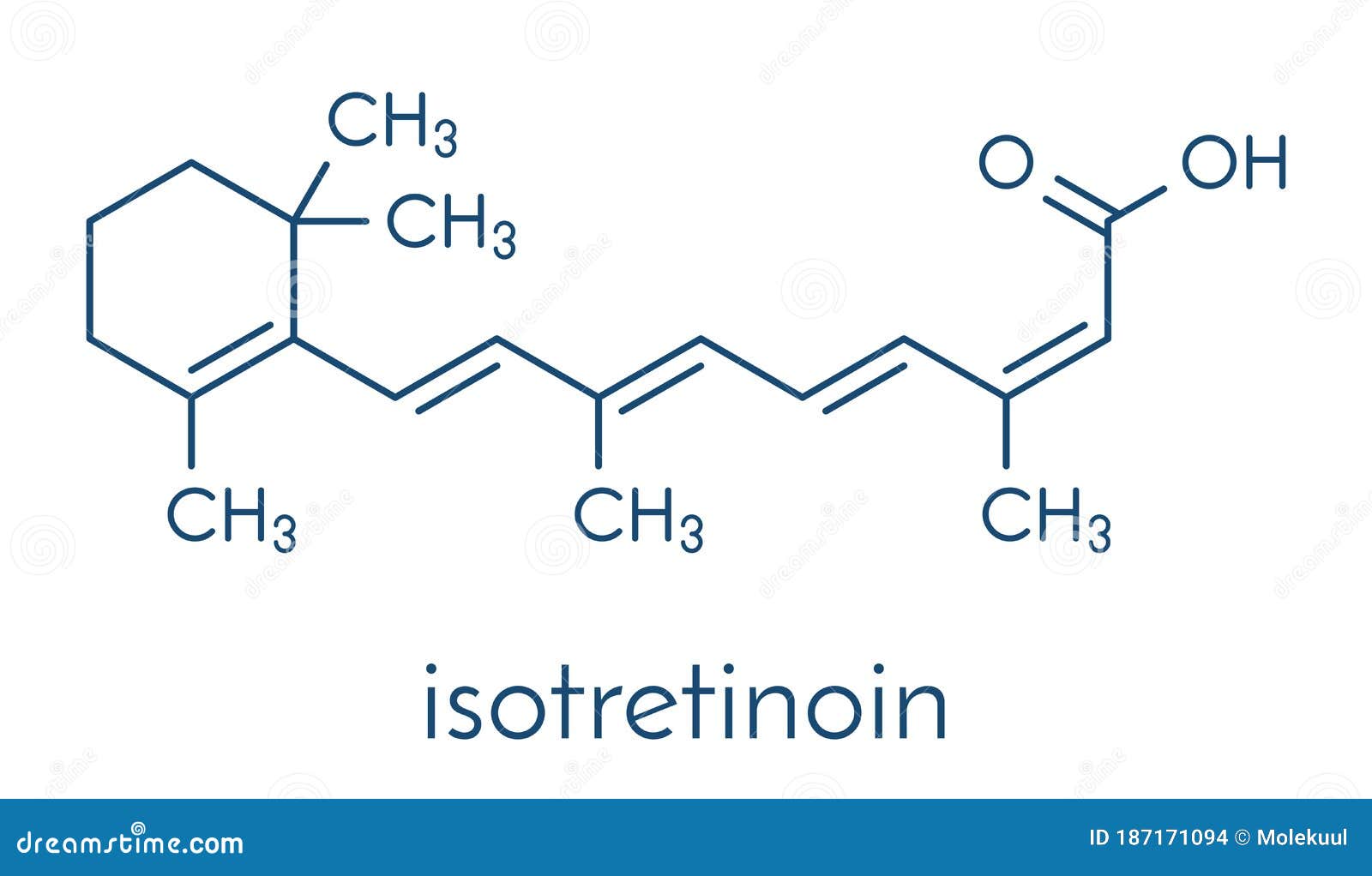
Isotretinoin Acne Treatment Drug Molecule Known Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 233194891 | Shutterstock

Low maternal vitamin A intake increases the incidence of teratogen induced congenital diaphragmatic hernia in mice | Pediatric Research

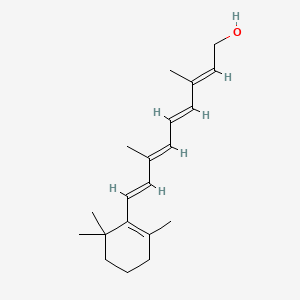
Bakuchiol, the Safer, Equally Effective Alternative to Retinol + Countertime Review — The Curious Coconut

Teratogen update: Topical use and third‐generation retinoids - Williams - 2020 - Birth Defects Research - Wiley Online Library