
LPS primed. (A) THP-1 cells and (B) BMDMs were stimulated with ATP. DHA... | Download Scientific Diagram
Effects of BJe on cytokine gene expression in THP-1 cells stimulated... | Download Scientific Diagram

LPS induces TNF-α production in PMA-treated THP-1 cells. THP-1 were... | Download Scientific Diagram

Potential anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effect of Coccinia grandis plant extract in LPS stimulated-THP-1 cells | SpringerLink

The Rate of Interleukin-1β Secretion in Different Myeloid Cells Varies with the Extent of Redox Response to Toll-like Receptor Triggering* - Journal of Biological Chemistry
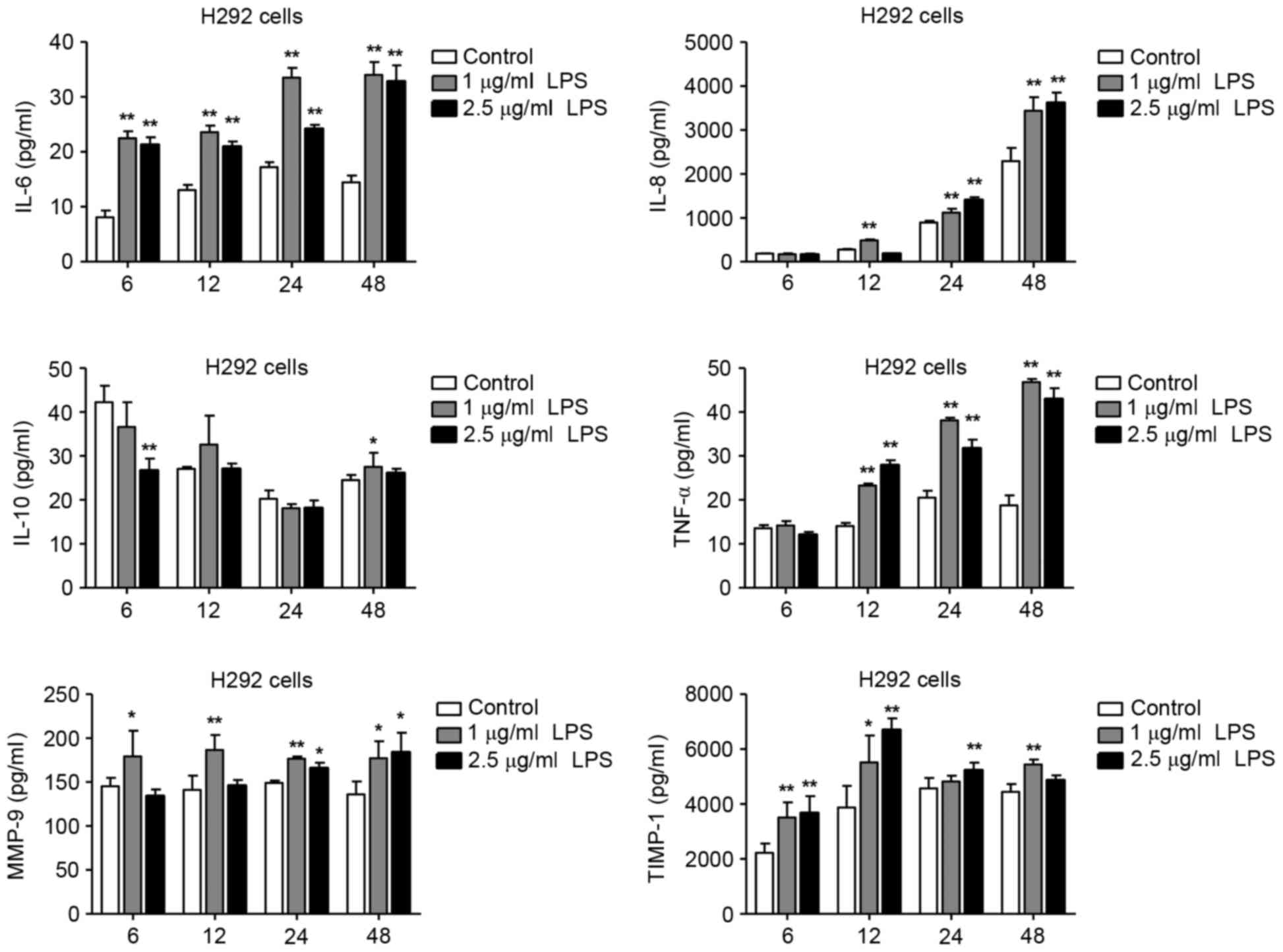
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Exposure of the Promonocytic Cell Line THP-1 to Escherichia coli Induces IFN-γ-Inducible Lysosomal Thiol Reductase Expression by Inflammatory Cytokines | The Journal of Immunology
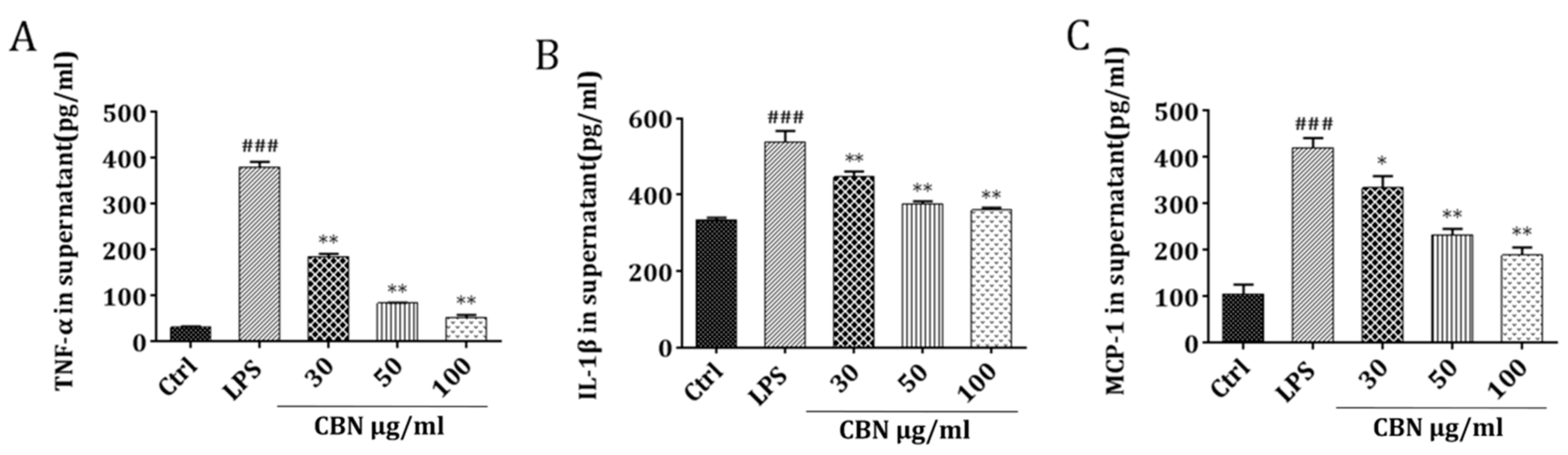
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Columbianadin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide ( LPS)-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis through the NOD1 Pathway | HTML

Crosstalk between signals initiated from TLR4 and cell surface BAFF results in synergistic induction of proinflammatory mediators in THP-1 cells | Scientific Reports
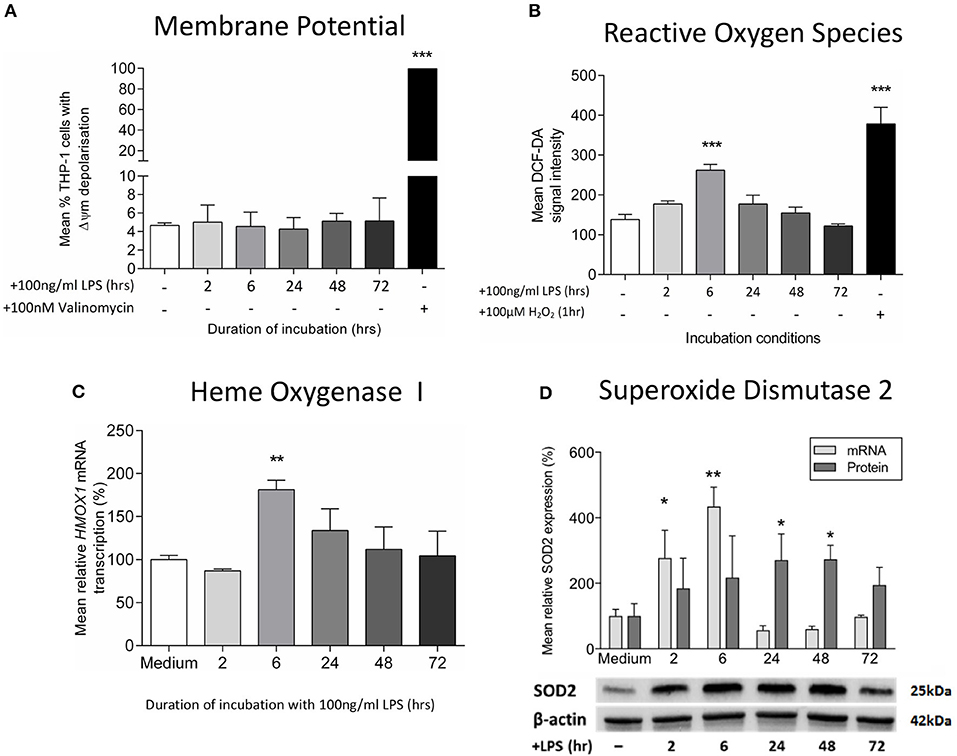
Frontiers | Exposure of Monocytic Cells to Lipopolysaccharide Induces Coordinated Endotoxin Tolerance, Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Mitophagy, and Antioxidant Defenses | Immunology
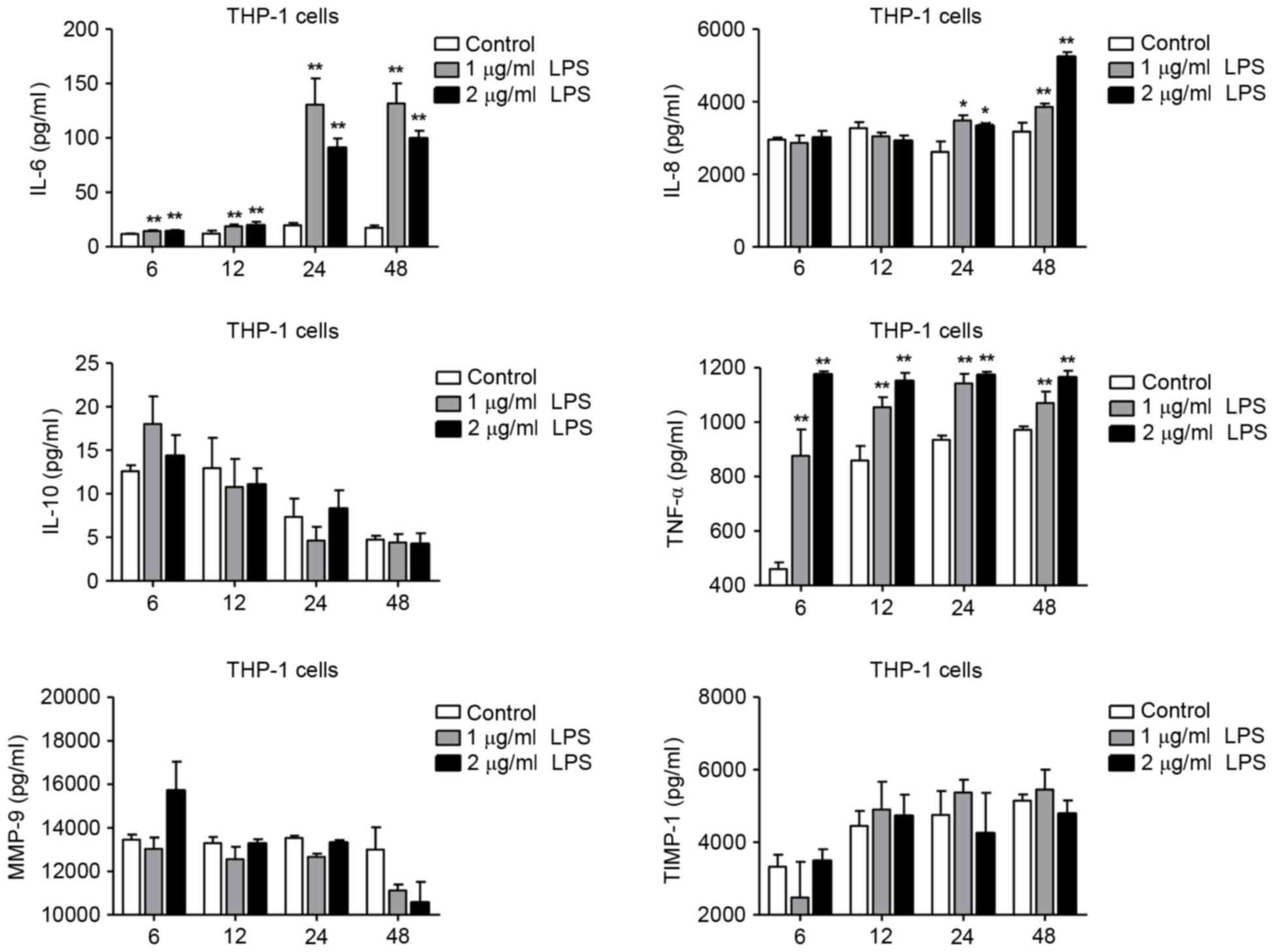
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Marine Drugs | Free Full-Text | Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Mytilus coruscus α-d-Glucan (MP-A) in Activated Macrophage Cells via TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK Pathway Inhibition | HTML
Type I Interferons Function as Autocrine and Paracrine Factors to Induce Autotaxin in Response to TLR Activation | PLOS ONE
Thrombospondin-1 Production Is Enhanced by Porphyromonas gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide in THP-1 Cells | PLOS ONE

LPS stimulation activates ATF4 in THP-1 cells. (a) The expression of... | Download Scientific Diagram

Differential Regulation of CD44 Expression by Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and TNF-α in Human Monocytic Cells: Distinct Involvement of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase in LPS-Induced CD44 Expression | The Journal of Immunology

Potential anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effect of Coccinia grandis plant extract in LPS stimulated-THP-1 cells | SpringerLink
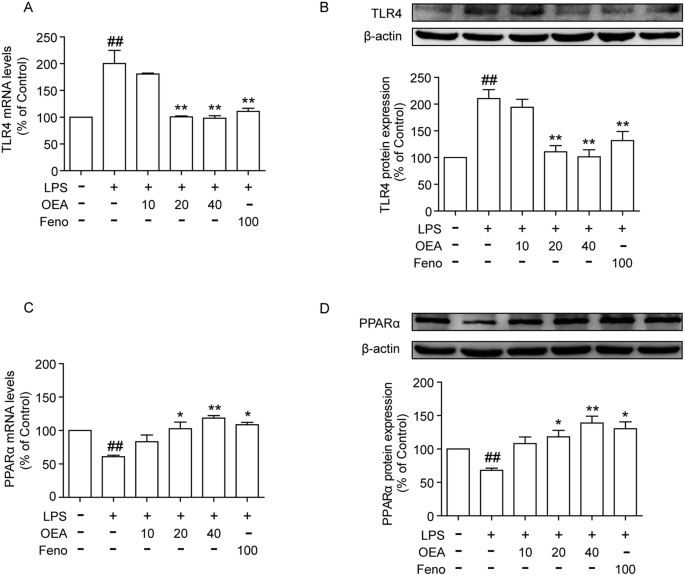
Oleoylethanolamide exerts anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced THP-1 cells by enhancing PPARα signaling and inhibiting the NF-κB and ERK1/2/AP-1/STAT3 pathways | Scientific Reports

Effect of LPS on gene expression in 5 ng/ml PMA-treated THP-1 cells.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Differentiation of Monocytes to Macrophages Primes Cells for Lipopolysaccharide Stimulation via Accumulation of Cytoplasmic Nuclear Factor κB | Infection and Immunity

Tetracyclines downregulate the production of LPS-induced cytokines and chemokines in THP-1 cells via ERK, p38, and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways - ScienceDirect

Standardized protocols for differentiation of THP-1 cells to macrophages with distinct M(IFNγ+LPS), M(IL-4) and M(IL-10) phenotypes - ScienceDirect
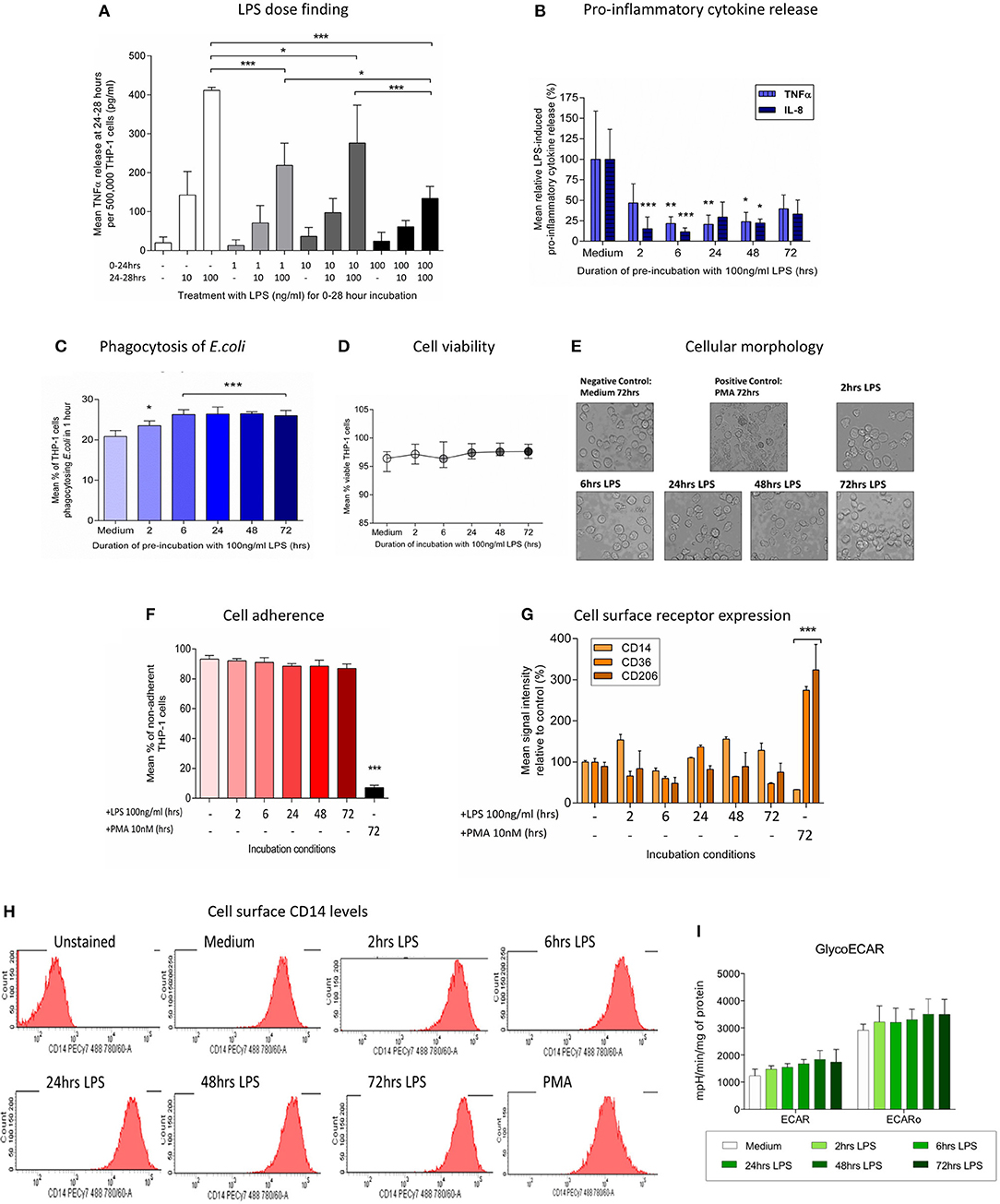
Frontiers | Exposure of Monocytic Cells to Lipopolysaccharide Induces Coordinated Endotoxin Tolerance, Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Mitophagy, and Antioxidant Defenses | Immunology

Oleoylethanolamide exerts anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced THP-1 cells by enhancing PPARα signaling and inhibiting the NF-κB and ERK1/2/AP-1/STAT3 pathways | Scientific Reports

Transcription profiles of LPS-stimulated THP-1 monocytes and macrophages : a tool to study inflammation modulating effects of food -derived compounds ... - Food & Function (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C0FO00113A


